Landing Zone networking using Terraform
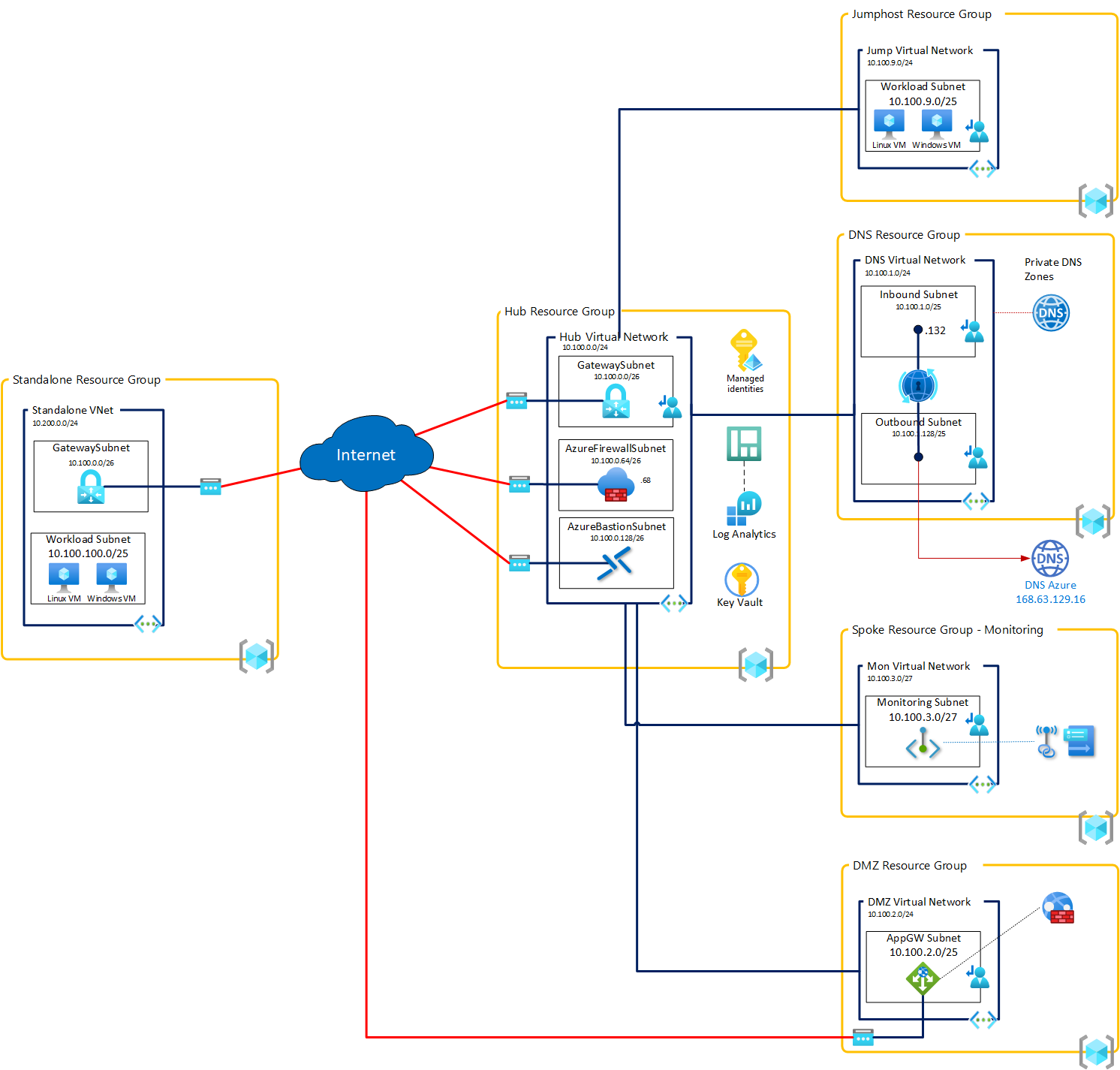
After more than one year at Microsoft, I spend lots of time to discuss network and landing zone design with my customers. Last summer, I start to work on some Terraform modules to help me on landing zone provisioning and in particular on network best practices while deploying a landing zone.
Disclamer : the code provided on this article and on my github are for demo purpose and will focus only on network part of the landing zone. If you want to deploy a production ready landing zone you can have a look on this projet : https://github.com/aztfmod/terraform-azurerm-caf
General presentation
This set of terraform modules will help you to create and manage Azure Resources and Azure Patterns.
The module can be used directly from the Terraform Registry.
Unit modules are available in the modules directory based on the resource name.
Composable/pattern modules are available in the modules directory with custom prefix.
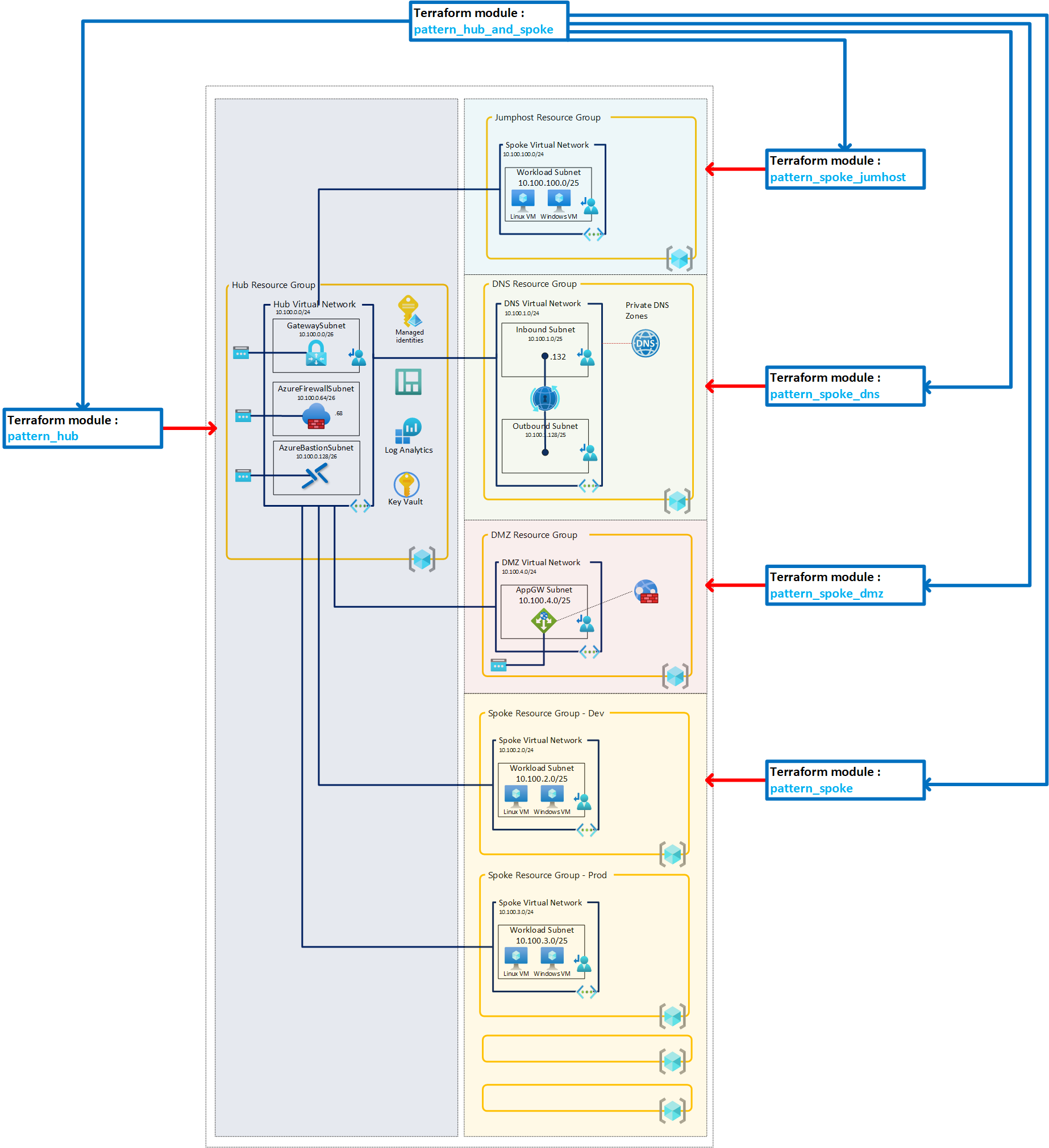
The main goal of this set was to deploy a full Hub and Spoke architecture based on best practices and my own experience. Naming of the resource is based on Azure naming convention.
How to deploy a basic "Hub & Spoke" topology ?
Let assume you want to provisioned the following architecture (even if at this stage it's not really useful or interesting) :
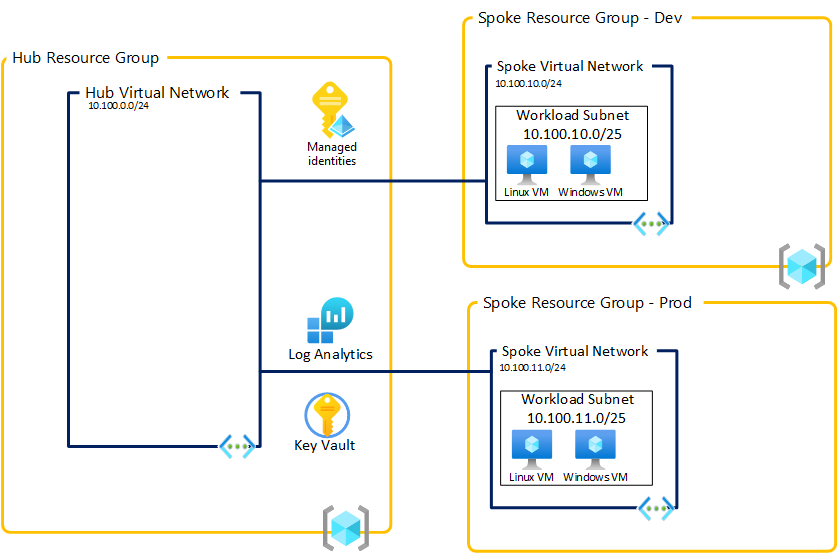
Using my terraform module it will be really simple :
terraform {
required_version = ">= 1.0.0"
required_providers {
azurerm = {
source = "hashicorp/azurerm"
version = ">=3.0.0"
}
}
}
provider "azurerm" {
features {}
}
module "hub_and_spoke" {
source = "azurerm/resources/azure//modules/pattern_hub_and_spoke"
location = "northeurope"
firewall = false
gateway = false
bastion = false
address_space_hub = ["10.100.0.0/24"]
address_space_spokes = [
{
workload = "app1"
environment = "dev"
instance = "001"
address_space = ["10.100.10.0/24"]
},
{
workload = "app1"
environment = "prd"
instance = "001"
address_space = ["10.100.11.0/24"]
}
]
}
Run "terraform init" then "terraform apply" and after few minutes you can expect to have this very basic hub & spoke infrastructure up and running. VM passwords will be stored in the KeyVault and username is : azureuser.
How to add a firewall in my hub and how to configure routing ?
terraform {
required_version = ">= 1.0.0"
required_providers {
azurerm = {
source = "hashicorp/azurerm"
version = ">=3.0.0"
}
}
}
provider "azurerm" {
features {}
}
module "hub_and_spoke" {
source = "azurerm/resources/azure//modules/pattern_hub_and_spoke"
location = "northeurope"
firewall = true
gateway = false
bastion = false
address_space_hub = ["10.100.0.0/24"]
address_space_spokes = [
{
workload = "app1"
environment = "dev"
instance = "001"
address_space = ["10.100.10.0/24"]
},
{
workload = "app1"
environment = "prd"
instance = "001"
address_space = ["10.100.11.0/24"]
}
]
}
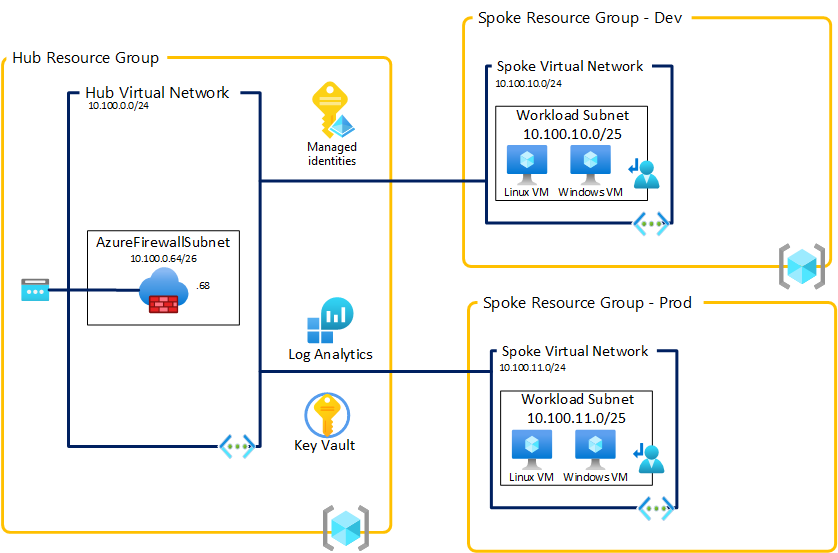
Adding the option "firewall = true" will provisioned an Azure Firewall in the hub and create all the routing configuration to pass through the firewall.
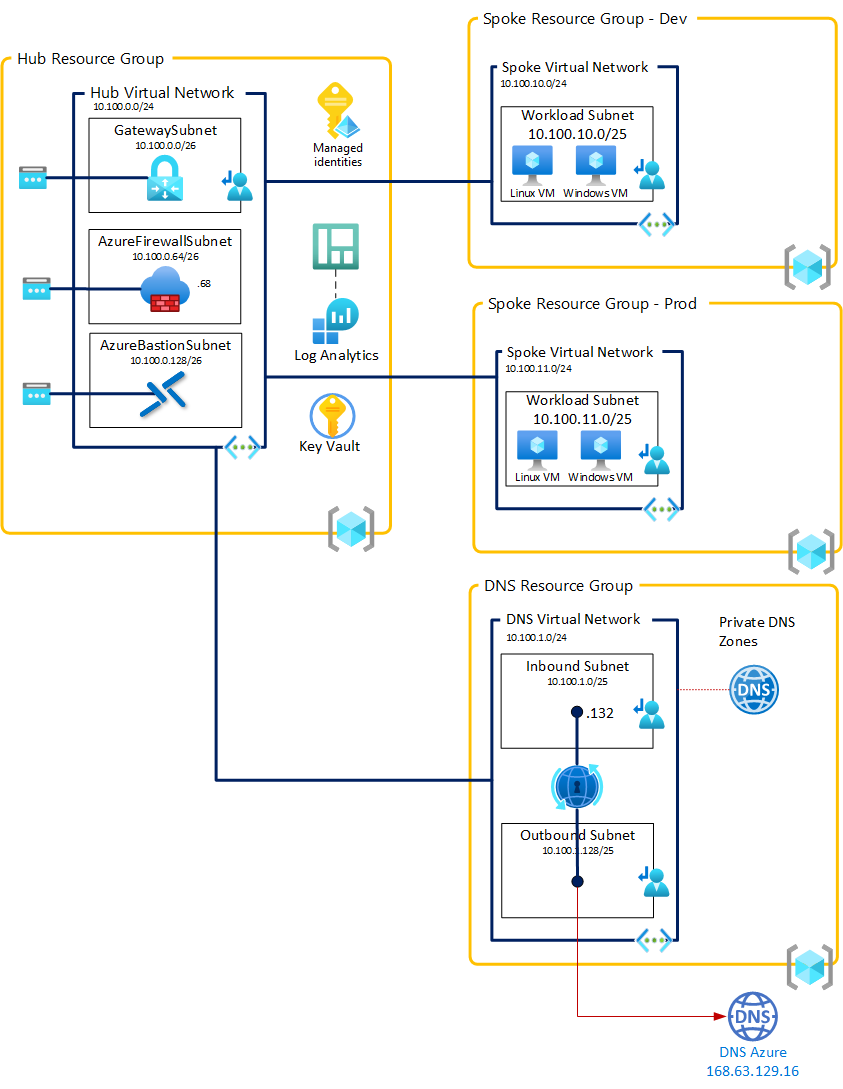
Do I need other services in my hub : DNS, proxy, bastion ?
That's a good question. My answer is simple, the only mandatory services in the hub are : gateway, firewall (or NVA) and bastion if you need it (Azure Bastion service is currently not compatible with custom routing). Other services can be placed on a shared service spoke or on dedicated spoke per service (my preferred choice).
Two main reasons for this : you can keep the security and the routing simple as you don't have to overwrite part of the hub VNet to pass through the firewall, if you want one day to move to Azure vWAN it will simplified your migration.
If you want to add all the services in your hub and create a spoke for DNS, it can be done like this :
terraform {
required_version = ">= 1.0.0"
required_providers {
azurerm = {
source = "hashicorp/azurerm"
version = ">=3.0.0"
}
}
}
provider "azurerm" {
features {}
}
module "hub_and_spoke" {
source = "azurerm/resources/azure//modules/pattern_hub_and_spoke"
location = "northeurope"
firewall = true
gateway = true
bastion = true
address_space_hub = ["10.100.0.0/24"]
spoke_dns = true
address_space_spoke_dns = ["10.100.1.0/24"]
address_space_spokes = [
{
workload = "app1"
environment = "dev"
instance = "001"
address_space = ["10.100.10.0/24"]
},
{
workload = "app1"
environment = "prd"
instance = "001"
address_space = ["10.100.11.0/24"]
}
]
}
It will take some time because of the gateway but at this end you must have the following architecture up and running :
How to expose web application on internet ?
If you want to expose a local web application, the recommended solution is to use two level of security : WAF + IDPS. If you want to achieve this in Azure, you can use Application Gateway with WAF + Azure Firewall Premium. If you want to test this using my Terraform module, it can be done using the following options :
terraform {
required_version = ">= 1.0.0"
required_providers {
azurerm = {
source = "hashicorp/azurerm"
version = ">=3.0.0"
}
}
}
provider "azurerm" {
features {}
}
module "hub_and_spoke" {
source = "azurerm/resources/azure//modules/pattern_hub_and_spoke"
location = "northeurope"
firewall = true
gateway = true
bastion = true
address_space_hub = ["10.100.0.0/24"]
spoke_dns = true
address_space_spoke_dns = ["10.100.1.0/24"]
spoke_dmz = true
address_space_spoke_dmz = ["10.100.2.0/24"]
web_application_firewall = true
address_space_spokes = [
{
workload = "app1"
environment = "dev"
instance = "001"
address_space = ["10.100.10.0/24"]
},
{
workload = "app1"
environment = "prd"
instance = "001"
address_space = ["10.100.11.0/24"]
}
]
}
If you don't required WAF, just configure "web_application_firewall = false" or just remove this line as by default WAF is not deployed.
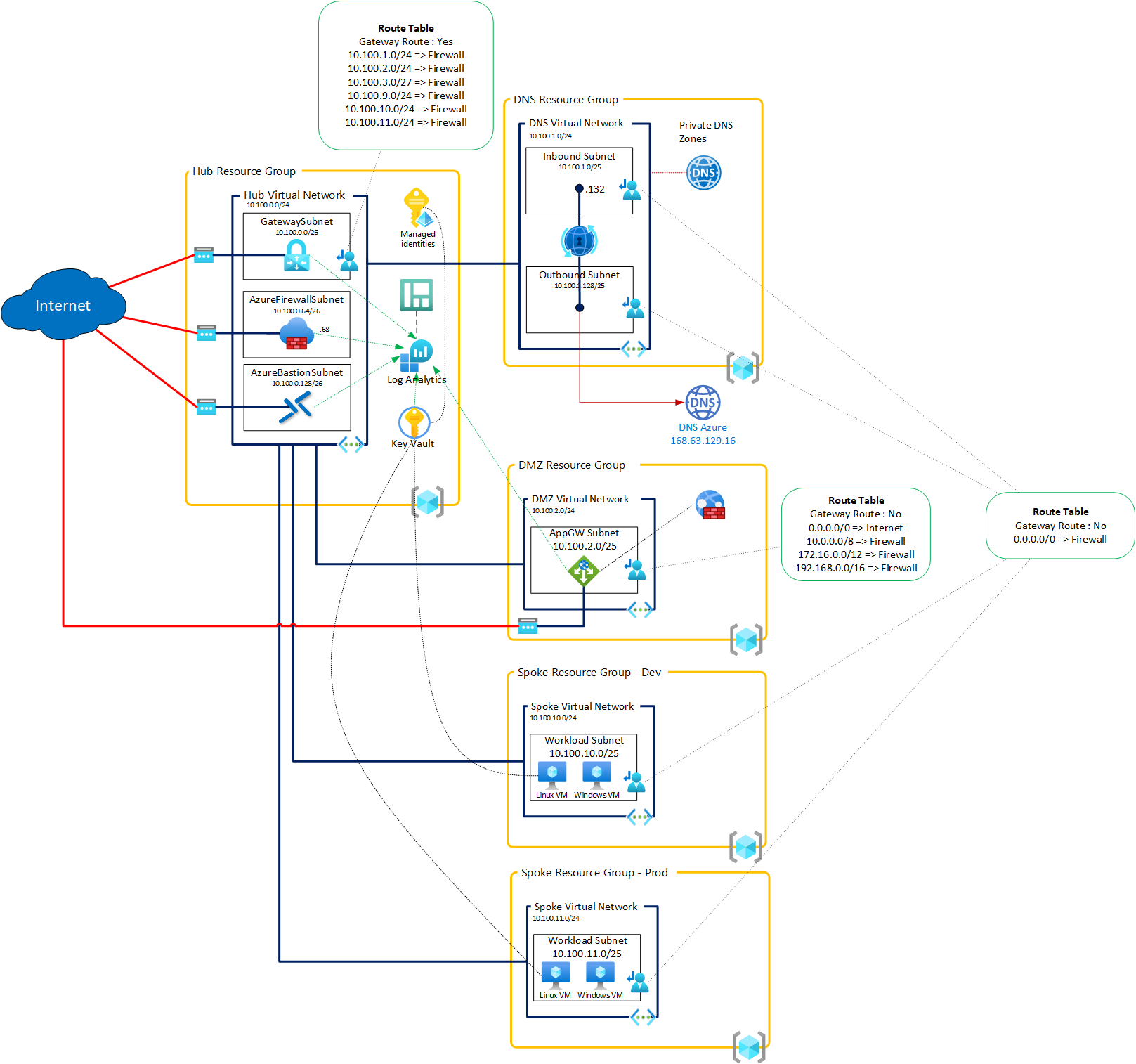
All the infrastructure is now ready to be configured : deploy a web server on any of the VM and configure the Application Gateway to expose this application on Internet (this part is not yet managed by the Terraform module).
Other options : private monitoring, connection monitor, ...
Additional options are available in the Hub and Spoke module :
- If you want to deploy Azure Monitor Agent (AMA) and use Private Link to connect to Azure Monitor (not easy to deploy the first time). Just add the following variables :
private_monitoring = true
address_space_spoke_private_monitoring = ["10.100.3.0/27"]
- If you want to deploy some Connection Monitor tests, you can add the following variable :
connection_monitor = true
- If you want to deploy another gateway to simulate an external site, you can use the following module :
module "standalone_site" {
source = "azurerm/resources/azure//modules/pattern_standalone_site"
location = "francecentral"
address_space = ["10.0.0.0/23"]
gateway = true
}
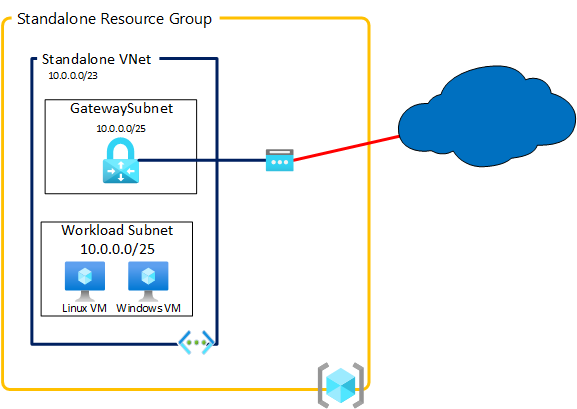
Conclusion
It takes me lots of time before having this result but I'm now using it almost every day and I can easily customize the architecture based on my needs and my tests.
More options are coming some so don't hesitate to update regularly the module to get the latest version: "terraform init -upgrade"
If you have any idea for new feature, don't hesitate to propose it directly on github and I will be happy to discuss it with you.